Microsoft Windows Event Log: Understanding the Microsoft Windows Event Log
- socanalystali
- Jan 16, 2024
- 2 min read
The Microsoft Windows Event Log functions as a digital chronicle, meticulously recording events, errors, and activities within the Windows operating system. It stands as a vital tool for system administrators, offering insights into the health, security, and performance of a Windows environment.
Purpose and Significance:
The Windows Event Log serves several essential purposes:
Diagnostic Insights: Acting as a diagnostic tool, it aids administrators in identifying and resolving issues related to system components, applications, and security.
Security Monitoring: Playing a pivotal role in monitoring security-related events, such as failed login attempts, denied access, or suspicious activities, it assists in the timely detection of potential security threats.
Performance Analysis: By logging events related to system performance, administrators can analyze trends, identify bottlenecks, and optimize the overall performance of the Windows system.
Troubleshooting: When issues arise, the Event Log provides a detailed history of events leading up to the problem, facilitating effective troubleshooting and issue resolution.
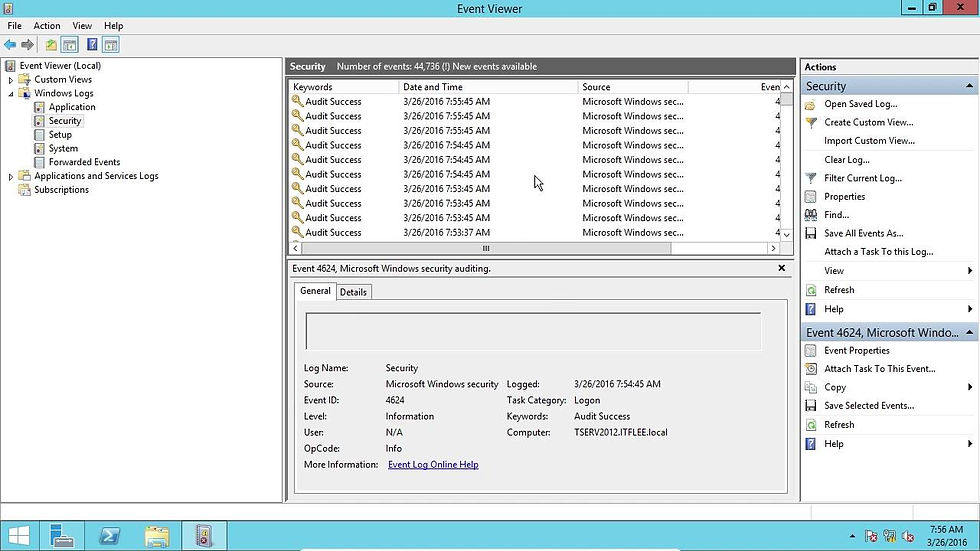
Accessing the Windows Event Log:
Accessing the Windows Event Log is straightforward through the built-in Event Viewer utility. Different logs can be accessed as follows:
Application Log:
Location: Windows Logs > Application
Purpose: Captures events generated by applications and services.
Security Log:
Location: Windows Logs > Security
Purpose: Records security-related events, including failed login attempts and access denials.
System Log:
Location: Windows Logs > System
Purpose: Logs events generated by the operating system and system services.
Setup Log:
Location: Windows Logs > Setup
Purpose: Documents events that occur during the Windows installation process.
Forwarded Events:
Location: Applications and Services Logs > Forwarded Events
Purpose: Displays events forwarded from other computers to the local computer.
Making the Most of Event Logs:
Administrators can optimize their use of Windows Event Logs by:
Creating Custom Views: Tailoring event log views based on specific criteria to focus on relevant information.
Setting Up Alerts: Configuring alerts to be notified of critical events or security incidents in real-time.
Integrating with Monitoring Tools: Integrating event logs with monitoring tools or Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems for centralized log management.
Conclusion:
In essence, the Microsoft Windows Event Log stands as a vigilant guardian, maintaining a meticulous record of the Windows environment's activities. Understanding its structure and accessing specific logs empowers administrators to uphold a secure, reliable, and high-performing Windows system.

Comentários